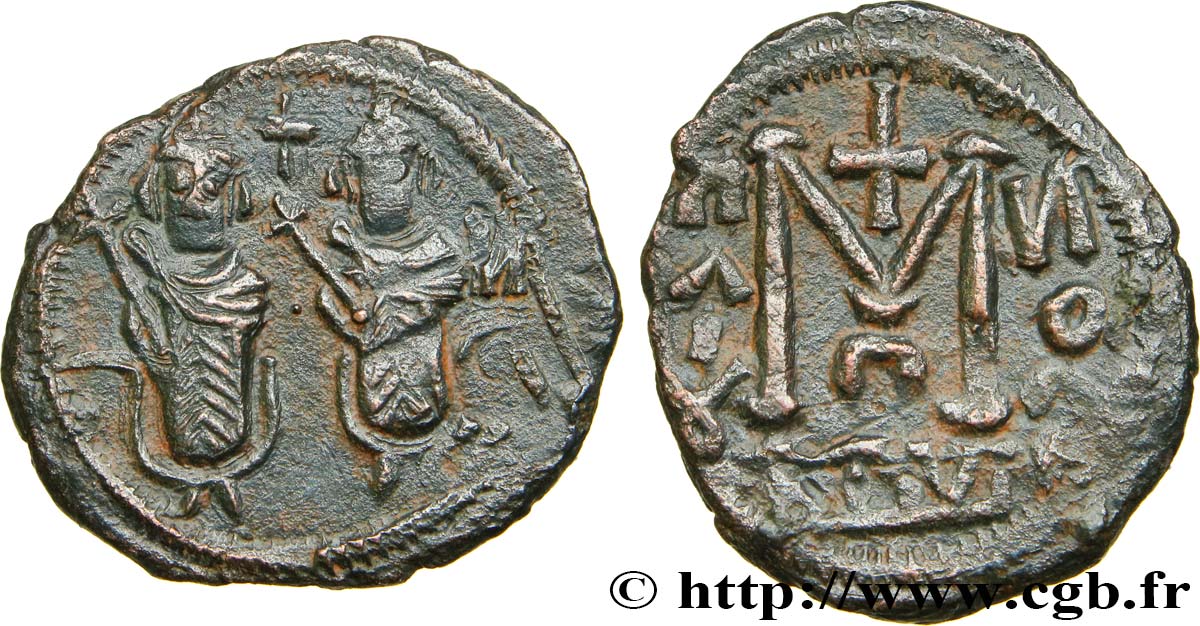
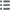
Obverse
Obverse legend : ANÉPIGRAPHE.
Obverse description : Deux personnages (empereurs) debout de face, couronnés, vêtus de la chlamyde tenant chacun une longue croix de la main droite.
Reverse
Reverse legend : INSCRIPTIONS ARABE ET GRECQUE.
Reverse description : Grande M stylisée.
Historical background
ARAB-BYZANTINE
(7th-8th centuries)
After the crushing of the Sassanid power, the Muslims swept over the Byzantine Empire less than ten years after the death of Muhammad (+ 632). Heraclius still lived long enough to see Muslim troops invade Syria, Palestine and Egypt. In the fall of 642, Egypt was definitively lost to Byzantium. It seems that the new invaders first kept the Byzantine monetary system of which they imitated the existing coins, which they named fals, distortion of fools. These imitations were manufactured for about fifty years as well as gold dinars, imitation of Byzantine solidi. Ali, fourth and last caliph of the line of Muhammad (he is at the same time his cousin, his foster brother and his son-in-law) sees his power challenged by Mo'awiya, governor of Syria, who has a well-trained army which defeated the Byzantines. Ali is defeated and murdered. The Umayyads, named after Omayya, father of Mo'awiya) established their capital in Damascus, and with them the elective nature of the office of caliph was lost.. The majority of believers, the Sunnis, accept this change. But the Muslims of the "party of Ali" ("shi'at Ali") or Shiites remain attached to the idea that only the descendants of Muhammad can claim the title of caliph, or rather of imam, a word which implies a power by divine right.








 Report a mistake
Report a mistake Print the page
Print the page Share my selection
Share my selection Ask a question
Ask a question Consign / sell
Consign / sell
 Full data
Full data















