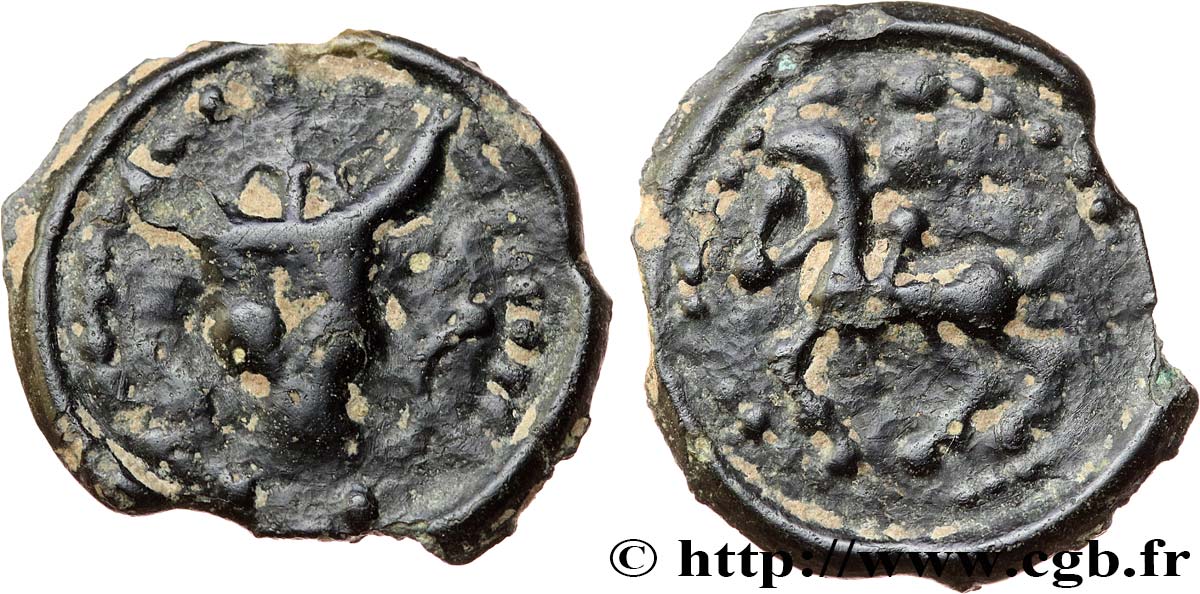
Live auction - bga_710579 - GALLIA - BITURIGES CUBI (Area of Bourges) Potin au bucrane et au cheval
You must signin and be an approved bidder to bid, LOGIN TO BID. Accounts are subject to approval and the approval process takes place within 48 hours. Do not wait until the day a sale closes to register. Clicking on "BID" constitutes acceptance of the terms of use of cgb.fr private live auctions.
Bids must be placed in whole Euro amounts only. The sale will start closing at the time stated on the item description; any bids received at the site after the closing time will not be executed. Transmission times may vary and bids could be rejected if you wait until the last second. For further information check the Live auction FAQ
All winning bids are subject to a 18% buyer’s fee.
All winning bids are subject to a 18% buyer’s fee.
| Estimate : | 200 € |
| Price : | no bid |
| Maximum bid : | no bid |
| End of the sale : | 26 April 2022 16:06:42 |
Type : Potin au bucrane et au cheval
Date: Ier siècle avant J.-C.
Metal : potin
Diameter : 18 mm
Orientation dies : 3 h.
Weight : 2,75 g.
Rarity : R3
Coments on the condition:
Monnaie centrée, avec un joli droit et un joli revers. Belle patine sombre
Predigree :
Monnaie vendue 260 euros lors de la vente CGB de Mars 2016
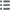
Obverse
Obverse legend : ANÉPIGRAPHE.
Obverse description : Bucrane accosté de deux esses, une croisette entre les cornes ; un grènetis en descendant d’une corne à l’autre et bourrelet périphérique.
Reverse
Reverse legend : ANÉPIGRAPHE.
Reverse description : Cavalier (?) à gauche ; grènetis perlé et bourrelet périphérique.
Commentary
Ce potin est très rare ; seulement connu par un exemplaire au musée de Zurich et de très rares en collections privées, c’est la seconde fois que nous le proposons à la vente après le bga_364110 de CELTIC 9 et nous n’en avons jamais vu passer d’autre en catalogues !
Le prototype du droit est clairement le potin des Rèmes au bucrane, lui-même inspiré du rare sesterce de Caius Antius Restio frappé vers 45 avant J.-C. Le revers au cheval n’a rien à voir avec l’ours du potin des Rèmes.
Le cavalier supposé n’est pas visible sur le n° 275 de Zurich (lui-même repris en dessin par A. Gaumann pour son n° 176). Le n° 24.5 de H. Patat correspond à notre monnaie, mais le cavalier pourrait n’être qu’une interprétation à partir de globules qui auraient fusé entre eux....
Le prototype du droit est clairement le potin des Rèmes au bucrane, lui-même inspiré du rare sesterce de Caius Antius Restio frappé vers 45 avant J.-C. Le revers au cheval n’a rien à voir avec l’ours du potin des Rèmes.
Le cavalier supposé n’est pas visible sur le n° 275 de Zurich (lui-même repris en dessin par A. Gaumann pour son n° 176). Le n° 24.5 de H. Patat correspond à notre monnaie, mais le cavalier pourrait n’être qu’une interprétation à partir de globules qui auraient fusé entre eux....








 Report a mistake
Report a mistake Print the page
Print the page Share my selection
Share my selection Ask a question
Ask a question Consign / sell
Consign / sell
 Full data
Full data









