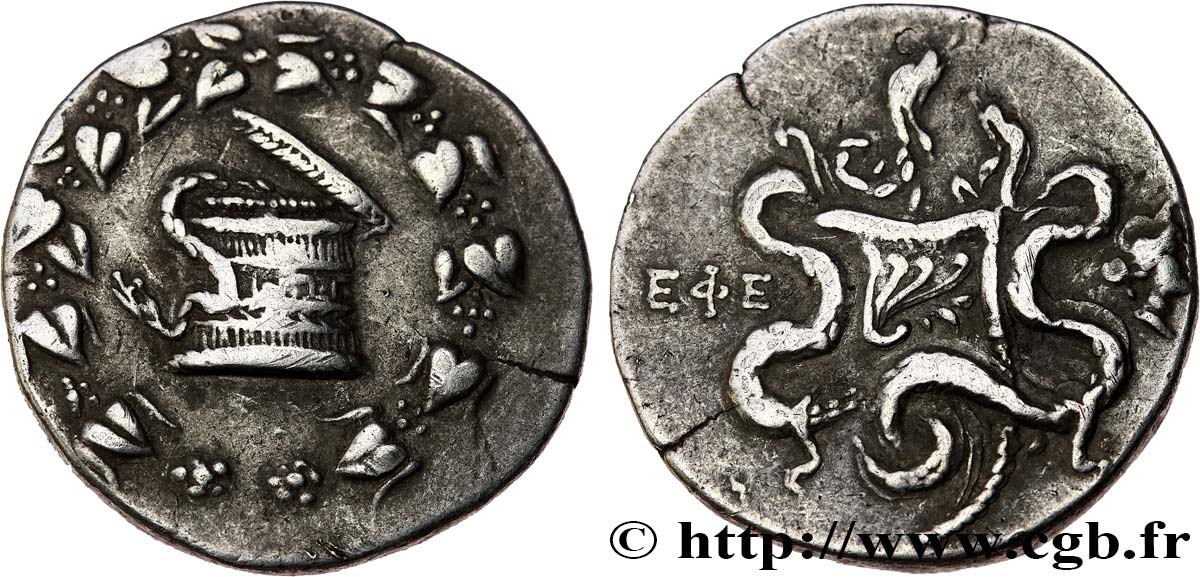
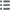
Obverse
Obverse legend : ANÉPIGRAPHE.
Obverse description : Ciste mystique de laquelle s'échappe un serpent ; le tout dans une couronne dionysiaque.
Reverse
Reverse description : Arc et goryte orné d'un aplustre entre deux serpents ; dans le champ à droite, une tête d’Artémis à droite.
Reverse legend : EFE
Reverse translation : (d’Éphèse).
Historical background
IONIA - EPHESUS
(3rd - 1st century BC)
Located at the mouth of the Caÿster on the coast of Asia Minor, Ephesus was famous for its temple dedicated to Artemis (Artemision) which could be dated, thanks to the votive deposit of construction, from the second half of the 7th century. The city suffered the Persian yoke. After the naval battle of Mycale in 479 BC. -VS. , it approached Athens and joined the Attico-Delian league from 477 BC. -VS. She broke with Athens after the disaster of Syracuse in 415 BC.. -VS. In 407 BC. -VS. , Lysander set up his headquarters in Ephesus and won the victory of Aegos-Potamos over the Athenians in 404 BC.. -VS. Spartan domination ceased after Conon's victory at Knidos in 394 BC. -VS. The Peace of Antalcidas in 387 BC. -VS. consecrated the city's return to Persian orbit. This domination lasted until 338 BC.. -VS. , date on which the city rose under the leadership of Philip II of Macedon. After Granicus in 334 BC. -VS. , the city rallied to Alexander after driving out the Persian garrison. In 295, the city fell into the hands of Lysimachus who renamed it Arsinoeia in honor of his wife, the daughter of Ptolemy. It regained its independence after the death of Lysimachus at Couroupédion in 281 BC.. -C and enjoyed a period of independence until 258 BC. -VS. , date on which, it entered for half a century under lagide domination before gaining once again a precarious autonomy. After 188 BC. -VS. , the city was integrated into the kingdom of Pergamon and followed its destinies until the bequest to Rome in 133 BC. -VS. .










 Report a mistake
Report a mistake Print the page
Print the page Share my selection
Share my selection Ask a question
Ask a question Consign / sell
Consign / sell
 Full data
Full data













