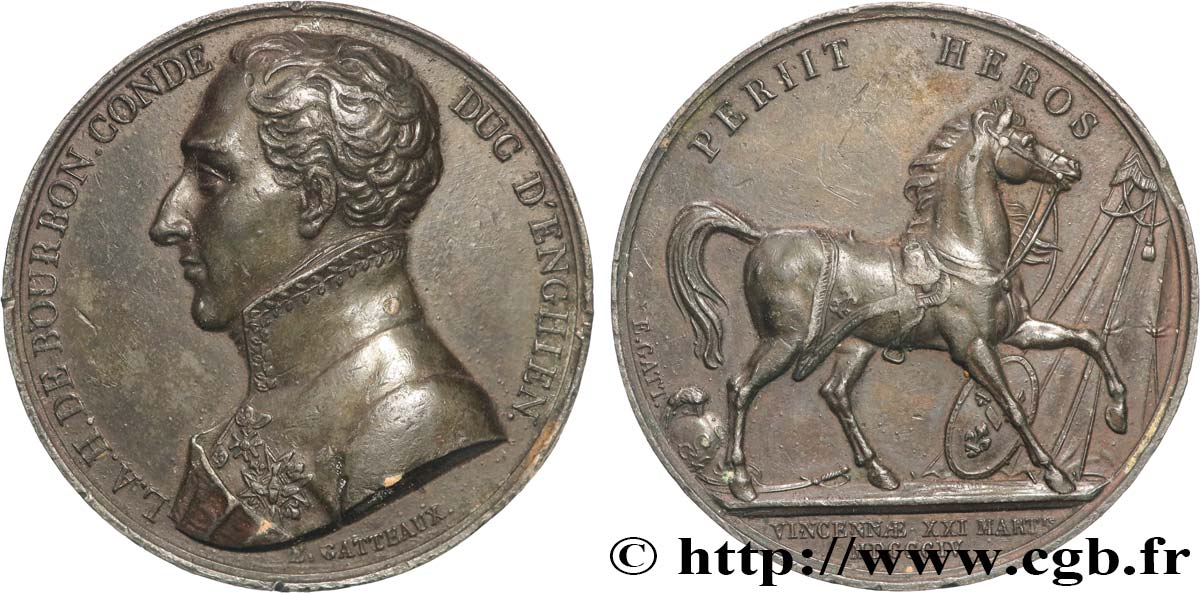
fme_888623 - PREMIER EMPIRE / FIRST FRENCH EMPIRE Médaille, Mort du Duc d’Enghien, Louis-Antoine-Henri de Bourbon-Condé
40.00 €(Approx. 43.20$ | 33.60£)
Quantity
Add to your cart

Type : Médaille, Mort du Duc d’Enghien, Louis-Antoine-Henri de Bourbon-Condé
Date: 1804
Metal : tin
Diameter : 40,5 mm
Orientation dies : 12 h.
Engraver GATTEAUX Jacques-Édouard (1788-1881)
Weight : 35,40 g.
Edge : lisse
Puncheon : sans poinçon
Coments on the condition:
Patine grise sombre hétérogène, présentant des coups et rayures, notamment sur la tranche. Coup de lime à 12 heures
Catalogue references :
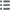
Obverse
Obverse legend : L. A. H. DE BOURBON. CONDE - DUC D’ENGHIEN..
Obverse description : Buste décoré à gauche du duc d’Enghien, signé : GATTEAUX.
Reverse
Reverse legend : PERIIT HEROS // À L’EXERGUE : VINCENNAE XXI MART.IS / MDCCCCIV.
Reverse description : Cheval à droite, près d’une tente d’armée ; un écu aux armes de France à ses pieds. Signé : E. GATT..
Commentary
Louis-Antoine-Henri de Bourbon-Condé (Chantilly, 1772 – Vincennes, 21 mars 1804) est un prince du sang français. Il est le 10e et dernier duc d'Enghien.
Fils unique de Louis, dernier prince de Condé et de Louise-Marie-Thérèse-Bathilde d'Orléans, il est le dernier descendant de la Maison de Condé.
Après un début d'union romanesque, ses parents se séparent en 1781. Sa mère est confinée au château de Chantilly.
Dès 1789, quelques jours après la prise de la Bastille et devant les troubles révolutionnaires, le jeune duc d'Enghien, âgé de 17 ans, rejoint l'Armée des émigrés qui se forme outre-Rhin sous le commandement de son grand-père, le prince de Condé et de son père, le duc de Bourbon. Le but de cette armée est de marcher sur la France pour restaurer l'Ancien Régime.
En 1792, le duc d'Enghien prend la tête de l'auto-proclamée Armée royale française. Cette dernière s'engage dans la tentative d'invasion (avortée) de la France aux côtés des armées alliées autrichienne et prussienne réunies sous le commandement du duc Charles-Guillaume Ferdinand de Brunswick. Néanmoins, Le 2 février 1794, il reçoit des mains du comte de Provence la Croix de Saint-Louis pour son comportement valeureux dans l'armée de Condé.
Il se réfugie à Ettenheim, dans le margraviat de Bade, à quelques lieues de la frontière française.
Ses projets de mariage avec la princesse Caroline de Bade ayant été contrariés par le margrave Charles-Frédéric, il vit ouvertement avec la femme de sa vie, Charlotte de Rohan-Rochefort.Napoléon Bonaparte, Premier Consul de France, le soupçonne d'être à l'origine d'un nouveau complot royaliste en compagnie de Dumouriez, à la suite d'une perquisition chez Armand de Chateaubriand (le cousin de François-René de Chateaubriand) qui fut fusillé plus tard. Il le fait enlever par une troupe de soldats menés par le général Ordener dans la nuit du 15 au 16 mars 1804.
Bonaparte ne tarde pas à découvrir la vérité, grâce à des papiers saisis par les membres de l'opération, prouvant que le duc d'Enghien porte les armes contre la République et envoie des assassins, par le biais de l'Angleterre, contre la personne du premier consul. Le duc est presque immédiatement traduit devant un conseil de guerre présidé par Pierre-Augustin Hulin. Après un simulacre de jugement, il est condamné à mort et fusillé dans les fossés du château de Vincennes le 21 mars 1804. Son corps est jeté dans une tombe creusée à l'avance au pied du pavillon de la Reine.
Fils unique de Louis, dernier prince de Condé et de Louise-Marie-Thérèse-Bathilde d'Orléans, il est le dernier descendant de la Maison de Condé.
Après un début d'union romanesque, ses parents se séparent en 1781. Sa mère est confinée au château de Chantilly.
Dès 1789, quelques jours après la prise de la Bastille et devant les troubles révolutionnaires, le jeune duc d'Enghien, âgé de 17 ans, rejoint l'Armée des émigrés qui se forme outre-Rhin sous le commandement de son grand-père, le prince de Condé et de son père, le duc de Bourbon. Le but de cette armée est de marcher sur la France pour restaurer l'Ancien Régime.
En 1792, le duc d'Enghien prend la tête de l'auto-proclamée Armée royale française. Cette dernière s'engage dans la tentative d'invasion (avortée) de la France aux côtés des armées alliées autrichienne et prussienne réunies sous le commandement du duc Charles-Guillaume Ferdinand de Brunswick. Néanmoins, Le 2 février 1794, il reçoit des mains du comte de Provence la Croix de Saint-Louis pour son comportement valeureux dans l'armée de Condé.
Il se réfugie à Ettenheim, dans le margraviat de Bade, à quelques lieues de la frontière française.
Ses projets de mariage avec la princesse Caroline de Bade ayant été contrariés par le margrave Charles-Frédéric, il vit ouvertement avec la femme de sa vie, Charlotte de Rohan-Rochefort.Napoléon Bonaparte, Premier Consul de France, le soupçonne d'être à l'origine d'un nouveau complot royaliste en compagnie de Dumouriez, à la suite d'une perquisition chez Armand de Chateaubriand (le cousin de François-René de Chateaubriand) qui fut fusillé plus tard. Il le fait enlever par une troupe de soldats menés par le général Ordener dans la nuit du 15 au 16 mars 1804.
Bonaparte ne tarde pas à découvrir la vérité, grâce à des papiers saisis par les membres de l'opération, prouvant que le duc d'Enghien porte les armes contre la République et envoie des assassins, par le biais de l'Angleterre, contre la personne du premier consul. Le duc est presque immédiatement traduit devant un conseil de guerre présidé par Pierre-Augustin Hulin. Après un simulacre de jugement, il est condamné à mort et fusillé dans les fossés du château de Vincennes le 21 mars 1804. Son corps est jeté dans une tombe creusée à l'avance au pied du pavillon de la Reine.








 Report a mistake
Report a mistake Print the page
Print the page Share my selection
Share my selection Ask a question
Ask a question Consign / sell
Consign / sell
 Full data
Full data












