- Accueil
- >
- >
Live auction - fme_961692 - SECOND EMPIRE Médaille, Centenaire de l’empereur Napoléon Ier
You must signin and be an approved bidder to bid, LOGIN TO BID. Accounts are subject to approval and the approval process takes place within 48 hours. Do not wait until the day a sale closes to register. Clicking on "BID" constitutes acceptance of the terms of use of cgb.fr private live auctions.
Bids must be placed in whole Euro amounts only. The sale will start closing at the time stated on the item description; any bids received at the site after the closing time will not be executed. Transmission times may vary and bids could be rejected if you wait until the last second. For further information check the Live auction FAQ
All winning bids are subject to a 18% buyer’s fee.
All winning bids are subject to a 18% buyer’s fee.
| Estimate : | 100 € |
| Price : | no bid |
| Maximum bid : | no bid |
| End of the sale : | 17 December 2024 14:51:22 |
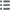
Type : Médaille, Centenaire de l’empereur Napoléon Ier
Date: 1869
Mint name / Town : 75 - Paris
Metal : gilt copper
Diameter : 50,5 mm
Orientation dies : 12 h.
Weight : 43,19 g.
Edge : lisse
Puncheon : sans poinçon
Coments on the condition:
Belle médaille dorée présentant quelques taches d’oxydation. Faible usure. Présence de quelques coups sur la tranche
Catalogue references :
Obverse
Obverse legend : SOUVENIR DU CENTENAIRE DE L’EMPEREUR NAPOLEON I // *1769=1869*.
Obverse description : Tête laurée de Napoléon Ier à droite.
Reverse
Reverse legend : ANÉPIGRAPHE.
Reverse description : Code Napoléon, posé un un coussin avec une légion d’honneur, un sabre et un chapeau bicorne, entre une branche de laurier et une branche de chêne ; au-dessus un aigle couronné tenant un foudre et une branche dans ses serres.
Commentary
Cette médaille est intéressante, représentant un résumé des symboles de ce que laissa Napoléon Ier.
- Le Code civil des Français, appelé usuellement « Code civil » (souvent abrégé en « C. Civ. » ou « CC ») ou « Code Napoléon », regroupe les lois relatives au droit civil français, c’est-à-dire l'ensemble des règles qui déterminent le statut des personnes (livre Ier), celui des biens (livre II) et celui des relations entre les personnes privées (livres III et IV).
- L’ordre national de la Légion d’honneur est l'institution qui, sous l'égide du grand chancelier et du grand maître, est chargée de décerner la plus haute décoration honorifique française. Elle a été instituée le 19 mai 1802 par Napoléon Bonaparte. Elle récompense depuis ses origines les militaires comme les civils ayant rendu des « mérites éminents » à la Nation.
En 2016, il existe 92 000 récipiendaires toujours vivants à comparer auprès d’un million de personnes ayant reçu cette décoration depuis sa création.
- Le Code civil des Français, appelé usuellement « Code civil » (souvent abrégé en « C. Civ. » ou « CC ») ou « Code Napoléon », regroupe les lois relatives au droit civil français, c’est-à-dire l'ensemble des règles qui déterminent le statut des personnes (livre Ier), celui des biens (livre II) et celui des relations entre les personnes privées (livres III et IV).
- L’ordre national de la Légion d’honneur est l'institution qui, sous l'égide du grand chancelier et du grand maître, est chargée de décerner la plus haute décoration honorifique française. Elle a été instituée le 19 mai 1802 par Napoléon Bonaparte. Elle récompense depuis ses origines les militaires comme les civils ayant rendu des « mérites éminents » à la Nation.
En 2016, il existe 92 000 récipiendaires toujours vivants à comparer auprès d’un million de personnes ayant reçu cette décoration depuis sa création.








 Report a mistake
Report a mistake Print the page
Print the page Share my selection
Share my selection Ask a question
Ask a question Consign / sell
Consign / sell
 Full data
Full data










