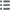
Obverse
Obverse legend : + LVDOVICVS* DEI GRA* FRANCOR* REX (MM), (PONCTUATION PAR SIMPLE MOLETTE).
Obverse description : Trois lis posés 2 et 1 sous une couronne.
Obverse translation : (Louis, par la grâce de Dieu, roi des Francs).
Reverse
Reverse legend : + SIT* NOMEH* DOMINI* BENEDICTVM (MM), (PONCTUATION PAR SIMPLE MOLETTE).
Reverse description : Croix fleurdelisée.
Reverse translation : (Béni soit le nom du Seigneur).
Historical background
LOUIS XI THE "PRUDENT"
(07/22/1461-08/30/1483)
Born in Bourges in 1423, Louis XI spent his early years in Loches. From 1439, Charles VII associated it with power. The first break with his father occurred in 1440, during the Praguerie. After which, Louis fought against the English and the Armagnacs. New revolt in 1446: Louis tried to seize the Agenais, and, the following year, his father exiled him in Dauphiné. The Dauphin ruled this province wisely and in 1453 erected the Dolphin Council in Parliament. Still scheming against his father, he married Charlotte of Savoy in 1451. In 1456, he took refuge with Philippe le Bon, the powerful Duke of Burgundy. The death of Charles VII prevented a war between the king and his powerful vassal. It was accompanied by Philippe that Louis XI entered Reims to be crowned there in August 1461.. After having reached Paris together, they separated and Louis settled in Touraine.. Thirty-eight-year-old the new king was as cunning and thrifty as the duke was glitzy and no-nonsense.. He dismissed his father's advisers and replaced them, among others, with the bastard of Armagnac and Pierre de Morvilliers.. "Universal aragne", the king built up a powerful network of followers. Very quickly, Louis XI came up against the feudal lords, his former allies. The "War of the Public Good", in 1465, brought together several vassals under the leadership of Charles de Berry, the king's brother. By the Treaty of Conflans and Saint-Maur (October 1465). Louis had to cede Normandy to his brother, the towns of the Somme to Charles the Bold, son of the Duke of Burgundy, and give the lieutenancy general of the central provinces to Louis de Bourbon. The king soon regained the advantage, taking advantage of the troubles that followed the death of Philip the Good (1467). A prisoner of the Téméraire for a moment during the interview at Péronne (October 1468), Louis XI had to remove Flanders from the jurisdiction of the Paris Parliament and attend the capture of Liège, whose revolt he had supported against the Burgundians.. Charles of France received Guyenne, but died in 1472. The war with Charles the Bold had resumed with renewed vigor. A truce was concluded in 1472. Jean V of Armagnac was defeated and killed at Lectoure (1473). The Duke of Alençon, arrested, died in 1476. The period of great feudal coalitions was over. The fight against the house of Burgundy, which was trying to erect a centralized state, independent of France and the Empire, a new Lotharingia, resumed secretly from 1473. In 1474, the Alsatians defeated and killed the Grand Bailiff of the Bold, Pierre de Hagenbach. In 1474, the Swiss and the Duke of Burgundy went to war: threatened with encirclement by the cantons and the French, Charles obtained a descent on the continent from the King of England, Edward IV. Louis XI stopped this danger by the peace of Picquigny (August 1475) and continued the liquidation of the feudal: the constable of Saint-Pol (1475), the duke of Nemours (1477). After concluding a truce with France, Charles the Bold seized Lorraine and wanted to take his revenge against the Swiss, whose armies Louis continued to finance: he was beaten at Grandson (March 1476) and Morat (June 1476). Fighting against revolted Lorraine, the Duke of Burgundy was beaten and killed in front of Nancy on January 5, 1477. His daughter Marie had to face the troubles of the Netherlands, while Louis XI annexed the two Burgundies, Picardy, Boulonnais and Artois. In 1477 the Bold's daughter married Maximilian of Austria. She died in 1482, leaving her husband as guardian of their son and heir Philippe le Beau.. A peace treaty was signed with France in December 1482. In 1480, on the death of King René, Louis had annexed Anjou and Bar. In 1481, on the death of Charles du Maine, Maine and Provence. The interior government of Louis XI remained famous for its authoritarianism. The Estates General only voted the tax without discussing. Three parliaments were created in Bordeaux (1462), Perpignan (1463) and Dijon (1477). To overcome the opposition of the Parliament of Paris, Louis XI evoked a number of political trials in the Council and handed them over to extraordinary commissions.. The fiscal pressure increased considerably to finance an incessant war. In 1472, a concordat was concluded with the Holy See; but the church of France was entirely in the hands of the king. Retired to Montil-lès-Tours after 1479, Louis XI devoted himself to a superstitious devotion, where the cult of relics had the greatest place.. He died on August 30, 1483 and was buried at Notre-Dame de Cléry. Married to Marguerite of Scotland then to Charlotte of Savoy, Louis XI had by the latter three children who survived him: Anne, married to Pierre de Beaujeu, Jeanne, who married Louis d'Orléans and Charles, a sickly child, who succeeded him..








 Report a mistake
Report a mistake Print the page
Print the page Share my selection
Share my selection Ask a question
Ask a question Consign / sell
Consign / sell
 Full data
Full data









