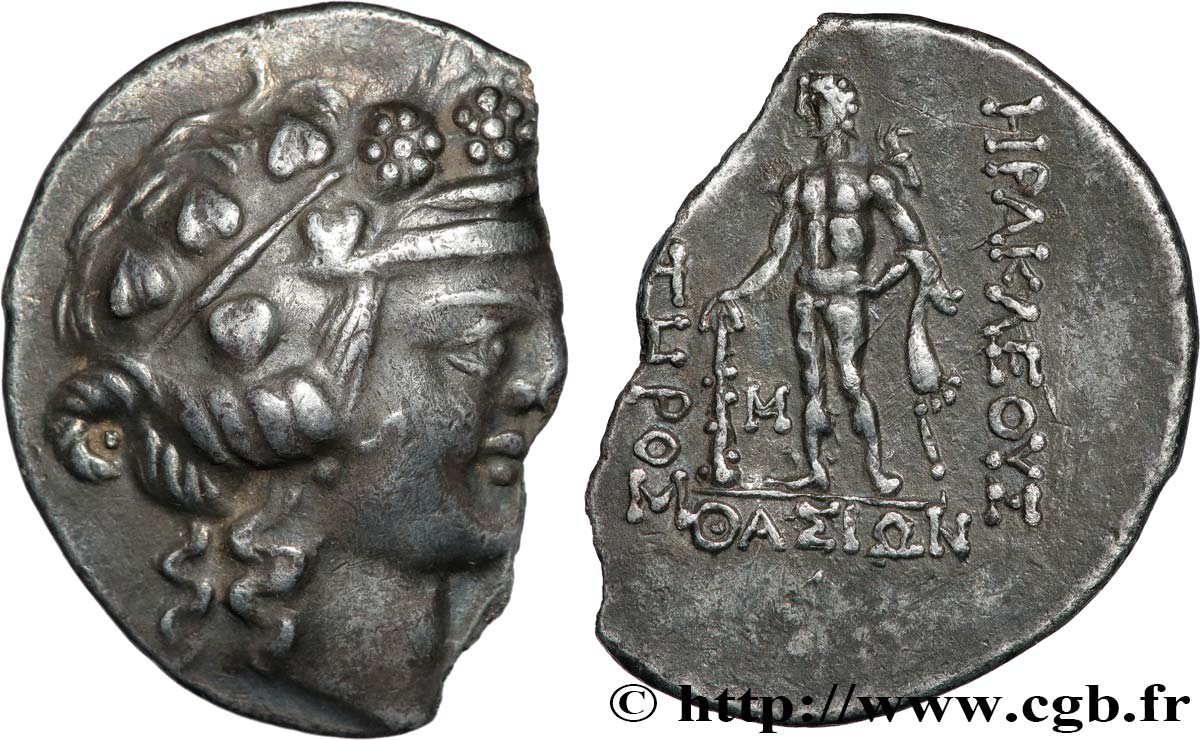
Obverse
Obverse legend : ANÉPIGRAPHE.
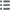
Obverse description : Tête de Dionysos à droite, portant une couronne de feuilles de vigne et de lierre, les cheveux longs.
Reverse
Reverse description : Hercule nu, la léonté flottant sur l'épaule, debout à gauche, tenant de la main droite la massue ; monogramme dans le champ à gauche.
Reverse legend : HRAKLEOUS // SWTHROS // QASIWN// (MP)
Reverse translation : (Hercule le grand de Thasos).
Historical background
THRACE - THRACIAN ISLANDS - THASOS
(2nd - 1st century BC)
Thasos was colonized by Ionians coming from Paros and was also visited by Phoenician sailors. The Sintian tribe occupied the island previously. The wealth of Thasos was proverbial thanks to the gold and silver mines of the island and neighboring Pangea which provided him with 200 to 300 talents of annual resources according to Herodian (VI, 46). During the revolt of Thrace in 498 BC. -VS. against the Persian Empire, Darius I (521-486 AC. ) wanted to impose the city. After the Persian Wars, Thasos entered into the Athenian alliance and the proceeds of the mines were diverted to benefit first the Delian League, then Athens directly. In 411 BC. -VS. , Thasos revolted and drove out the Athenians who were immediately replaced by a Spartan garrison. After 357 BC. -VS. , Thasos fell under Macedonian rule. It regained part of its independence with the death of Lysimachus in 281 BC.. -VS. After the defeat of Cynoscephales in 197 BC. -VS. , Thasos became autonomous again. From 148 or 146 BC. -VS. , the Roman Senate authorized Thasos and Maronea to mint wide blank tetradrachms which were minted in very large quantities and imitated in the Balkans until the end of the 1st century BC.. -VS.










 Report a mistake
Report a mistake Print the page
Print the page Share my selection
Share my selection Ask a question
Ask a question Consign / sell
Consign / sell
 Full data
Full data















